Nevada is the only state producing lithium in the U.S.
Lithium staking has become the “Gold Rush” of the 21st century in Nevada.
Mining is vital to the economy with vast operations throughout the state.
1 – Price, J.G., Lechler, P.J., Lear, M.B., and Giles, T.F., Possible volcanic source of lithium in brines in Clayton Valley, Nevada, in Cluer, J.K., Price, J.G., Struhsacker, E.M., Hardyman, R.F., and Morris, C.L., eds., Geology and Ore Deposits (2000) Note: (2) Reference Holly Street Capital Inc. press release dated November 1, 2021 for additional details
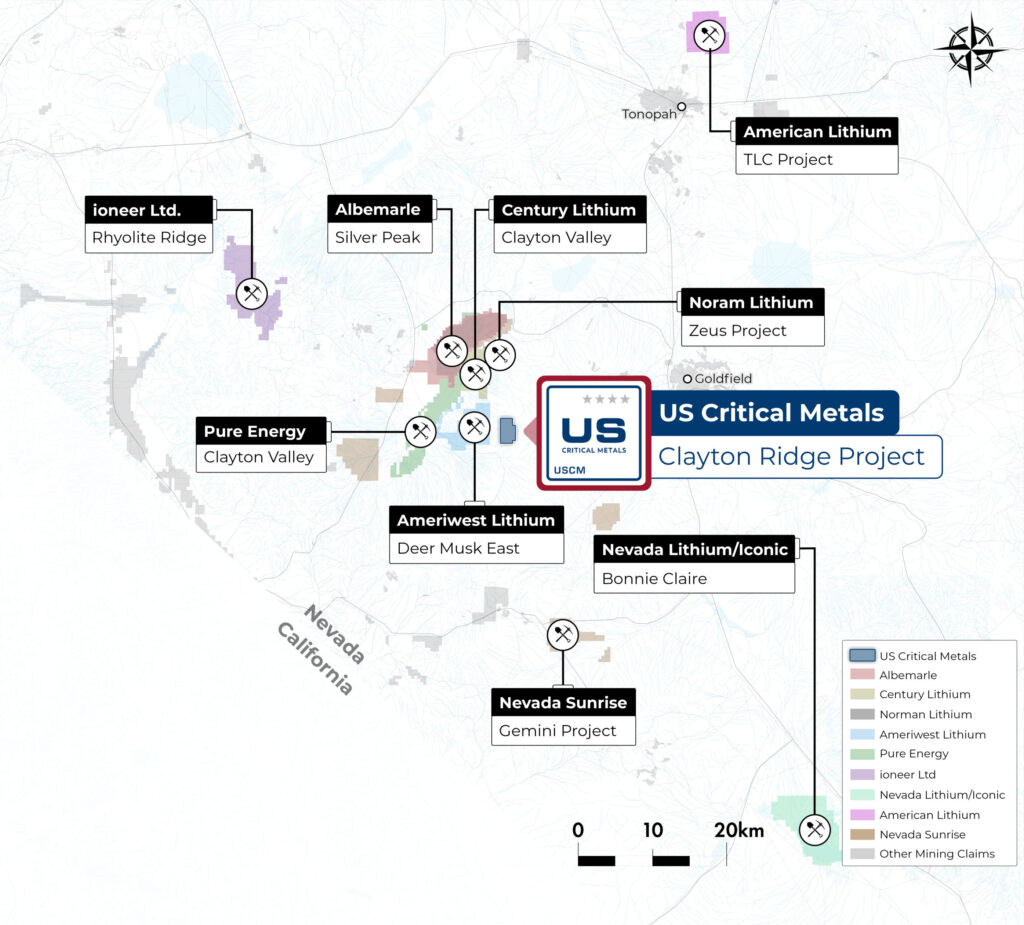
Clayton Ridge has been speculated as the source of lithium brine in Clayton Valley. This project was generated by the prospector that initially sourced certain claims for American Lithium Corp. and ioneer Ltd.
Lithium claystone property located in a hanging basin above Clayton Valley, Nevada.
Initial grab samples report values up to 950ppm lithium.
Geologic model possibly similar to lithium claystone deposit of Cypress Development Corp.
USCM has the right to earn 100% interest on 180 contiguous claims
(~3,600 acres).
Potential caldera-hosted deposit with intrusive dikes penetrating the claystone on the northeast of the property.
Gravity survey over the region in 2011 and 2012 by Hasbrouck Geophysics identified a large gravity low anomaly.
USCM is situated close to companies that have billions in combined market capitalizations. Clayton Valley and surrounding areas have been a focal point of lithium exploration, development, and production in the US for over 50 years.
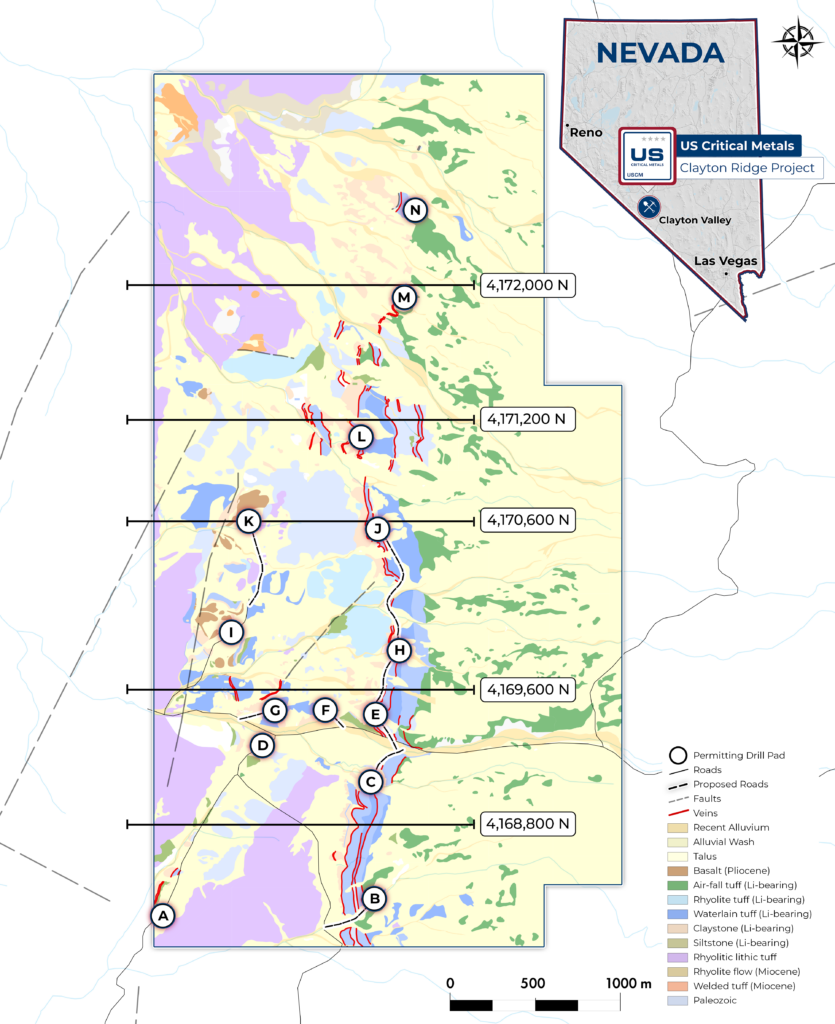
Lithium-bearing sediments located in an uplifted basin east of the Clayton Valley.
At least two lithium-rich claystone units merge to the north into a broad package of prospective sediments.
Lithium-bearing claystone units have been mapped over the entire length of the Clayton Ridge claim block, roughly 7 kilometers.
The prospective horizons are both floored and capped by rhyolitic lithic tuffs and air fall tuffs, respectively.
Lithium extraction from brines pioneered in Clayton Valley about 50 years ago.
Significant increase in regional activity driven by US demand for electric vehicles.
New deposits discovered outside existing basin boundary utilizing geophysical and ground exploration techniques.
Significant amounts of capital invested into exploration, development, and production of lithium in the region.
| Company/Listing | Rhyolite | Clayton Valley | Clayton Ridge | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Valuation | ioneer Ltd. AUX: INR |
Century Lithium Corp. TSXV: LCE |
US Critical Metals Corp. TSX:USCM |
NA |
| Location | $713M (AUD/CAD: $0.93) | $138 (basic) | $12M (basic) | USCM discount due to asset stage |
| Stage | 931 acres Mountain basin above Fish Valley, Nevada |
5,585 acres Near slope rising to Clayton ridge, Clayton Valley, Nevada |
3,600 acres Mountain basin above Clayton Valley, Nevada |
Proximate projects in Nevada. Similar acreage position |
| Deposit Type | Feasibility (NPV at 8% of US$1.3B Unleveraged IRR of 20.8%) |
Pre-Feasibility (NPV at 8% of US$1.0B USD / Unleveraged IRR of 25.8%) |
Drill Ready Plans to drill in 2023 |
Homogeneous deposits. Potential to build resource and economics rapidly |
| Deposit | Caldera-hosted deposit with interlayered sedimentary and volcanic rocks. | Caldera-hosted deposit with interlayered sedimentary and volcanic rocks. | Possibly caldera-hosted deposit with interlayered sedimentary and volcanic rocks. | Drilling required to validate deposit type. Nearly identical rock type |
| Characteristics | Attributable LCE of 0.6Mt and M&l + lnferred 1.3Mt. | Attributable LCE of 0.6Mt and M&l + lnferred 1.3Mt. | Samples of up to 950ppm, lithium claybeds throughout, estimated thickness of 100-200 meters. | Regional has been demonstrated to produce large resource deposits |
Note: The Company’s Qualified Person(s) have not verified the geological information pertaining to other adjacent and/or comparable properties. The information about mineralization on
adjacent properties is not indicative of mineralization on the Clayton Ridge Project. See “Comparables” on slide 2 Source: Disclosed company materials and market information (as of May 31, 2023).
1 – information referenced from: www.ioneer.com, www.centurylithium.com, www.uscriticalmetals.com
The primary goal of this phase is to assess shallow, east-dipping lithium-bearing units by using west-dipping holes. The intent is to ascertain the thickness and grade of these units.
Final drill targets refined and approved by BLM. Up to 5 acres of disturbance area permitted.
Additional acreage to be further explored and drilled based on phase 1 results.
Excellent potential to build tonnage. Mapping indicates Li units containing over 200 meters of thickness.
Sampling completed at surface show grades warranting further exploration across the basin and at depth.
Note: A USCM Qualified Person has not done enough work to verify the results of the historical exploration
Targets A to G The southern unit of the property shows high lithium potential, with lithium found up to 200m deep in five geological formations. This shows high grade lithium potential.
Targets H to K Designed to test the central portion of the property, which overlies older dolomitic rocks in the center of the property. These lithium-bearing units also comprise air-fall tuff, rhyolite tuff, water-lain tuff, claystone and siltstone.
Targets L to N Designed to test rock chip anomalies to the north and potentially extend mineralization in that direction. These holes will be drilled subject to permitted disturbance area available.
US controls 3.6% of total world-wide lithium reserves yet is expected to account for a significant amount of demand for the unplanned new supply requirements needed to fuel the EV industry.
1 – United States Geological Survey: Rare Earths Data Sheet, Mineral Commodity Summaries (2020), 2 – Darton Commodities Ltd., Lithium Market Review (2020-2021)
© 2025 US Critical Metals Corp. All rights reserved
Maps, Deck and Site by ExplorationSites.com
